When searching for a steam source solution for your business, you probably have come across two common systems that sound similar: electric steam generators and steam boilers. Although they both produce steam for a variety of uses, there are many differences between the two systems, especially with the way they operate. Understanding these differences and the design of both systems will help you determine the right one for your process needs.
What Is a Steam Generator?
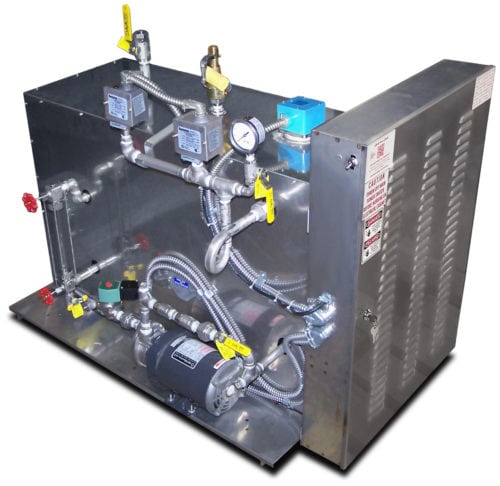

Most steam generators feature a single coil and have a once-through, forced-flow design. Any excess water that doesn’t convert to steam collects into a filter for reuse or disposal, and excess gasses can also travel through the generator for easy release. The design makes the steam generator simple and easy for small to moderate amounts of steam generation.
What Is a Steam Boiler?
Steam boilers are similar to steam generators, but they operate on a much larger scale (and with a more intricate design as a result). They are used in large commercial or industrial operations that need more steam output than most steam generators can provide. They have a complex fuel system and pressure vessels that can withstand high pressure levels, which allows them to convert water to steam by boiling water at subcritical temperatures.
Because the systems are more complex, operate at potentially dangerous pressure levels, and create high volumes of hot steam, some buildings must have a licensed operator on-site the entire time the boilers are in operation. These individuals must hold certification regarding safety, operational requirements, and how to respond to emergencies and malfunctions.
There are two main types of steam boilers:
Firetube Boilers
Firetube boilers have a large water tank with multiple pipes running through the tank. The boiler also has a large fire, quickly burning fuel to heat up gasses running through the pipes until they reach very high temperatures. This heat then passes through the pipes into the stored tank water, where it causes the water to boil, convert to steam, and rise to the top of the tank. From there, the connecting systems can use the steam as energy for industrial or building processes.
Watertube Boilers
Watertube boilers are effectively the opposite of firetube boilers, and they are a newer alternative to traditional firetube constructions. Whereas firetube boilers have a tank of water and run heated gases through the tubes, watertube boilers instead have water from a reservoir run through the pipes. The body of the boiler houses multiple lengths of pipe filled with a continuous stream of water. Hot gas heated by a fire surrounds all of the tubes, and the heat transfers inside the tube to make the water boil and turn to steam. The steam rises to the top of the pipes, and the still-liquid water goes back to the reservoir before being sent back through the pipes for heating and conversion.
Advantages of Steam Generators
Steam generators are smaller, easier to install, and less potentially dangerous than steam boilers. Some of the specific advantages they provide are:
- Compact design: Their small footprint and simple design make it easier to set up a steam generator and get it running. This is ideal for emergency or on-demand steam generation.
- Ease of operation: Their simplicity means facilities can more readily take on operational and maintenance tasks. They also don’t require the on-site presence of a licensed and certified operator.
- Cost-effectiveness: Steam generators have a lower initial cost than steam boilers, as well as fewer maintenance and staffing costs.
- Efficiency: Steam generators are incredibly energy-efficient, achieving a nearly 100% electrical energy to heat energy conversion.
For smaller commercial steam requirements, emergencies, and on-demand steam systems, steam generators can be the right solution.
Advantages of Steam Boilers
Steam boilers are larger and more powerful than steam generators. This gives them several advantages, including the following:
- Greater steam production capabilities: Both types of steam boilers are larger, more powerful, and more capable of producing high volumes of steam.
- Dynamic steam generation: Steam boilers can also respond to fluctuating steam demands throughout work cycles, both producing more steam during busy cycles and quickly transitioning to producing less steam when less is needed.
- Can fulfill continuous steam demands: Once steam boilers reach optimal production levels, they can continuously meet high levels of demand.
Why Use a Steam Generator Over a Steam Boiler?
Many smaller processes that use steam do not need a large boiler. For those smaller processes, an easily portable steam generator would be the best tool for the job. A few of the top reasons to use an electric steam generator instead of a fuel-fired steam boiler include:
- Safety: Electric steam generators use no combustible fuel, therefore are not subject to major failures as fuel fired boilers are. Fossil fuel fired boilers can suffer failures from low conditions, poor water treatment, improper warm-up, pulling a vacuum, flame impingement, severe over-firing and even outright explosions.
- Portability: Steam generators have a smaller design that allows them to be used when facilities have limited space. Electro-Steam’s small-scale generators are portable and do not require extensive installation, such as boiler rooms and long steam lines
- Energy efficiency: Electric steam generators consume no energy while idle. When operational they only cycle when steam is needed. This is especially helpful in warmer months when full power may not be necessary. Fuel fired boilers require much more energy to run at full strength and, due to its larger design and extensive piping system, cannot easily be turned off and on and constantly burn fuel even when steam is not in demand
- Quick start: A steam generator’s compact design, single chamber, and relatively lower water demand allow these systems to achieve rated output in only minutes from a cold start, as opposed to boilers that can take hours. This quick-start capability makes a steam generator ideal for emergencies and instances where steam may not be needed for lengthy periods of time, such as pilot plants, labs and process testing.
- Cost: Installing a steam boiler system at your facility can be time-consuming and costly. Steam generators cost much less than a full-scale fuel fired boiler system, so they may work better for applications that do not require high levels of steam like those produced by boilers
Contact Electro-Steam Today
The winner of the steam generator vs. steam boiler debate will depend on the application and your facility’s energy production needs. We hope this short post will be helpful when deciding which system is right for you. Electro-Steam’s units are suited for both smaller steam required applications and large ones, in which boilers are used. If you have questions about or need information about our steam generators and steam boilers, contact Electro-Steam today. The Electro-Steam team will work with you to determine the system that will best fit your needs.
 Proudly Manufactured in the USA
Proudly Manufactured in the USA 
